‘Shortcuts everywhere’: How Boeing favored speed over quality
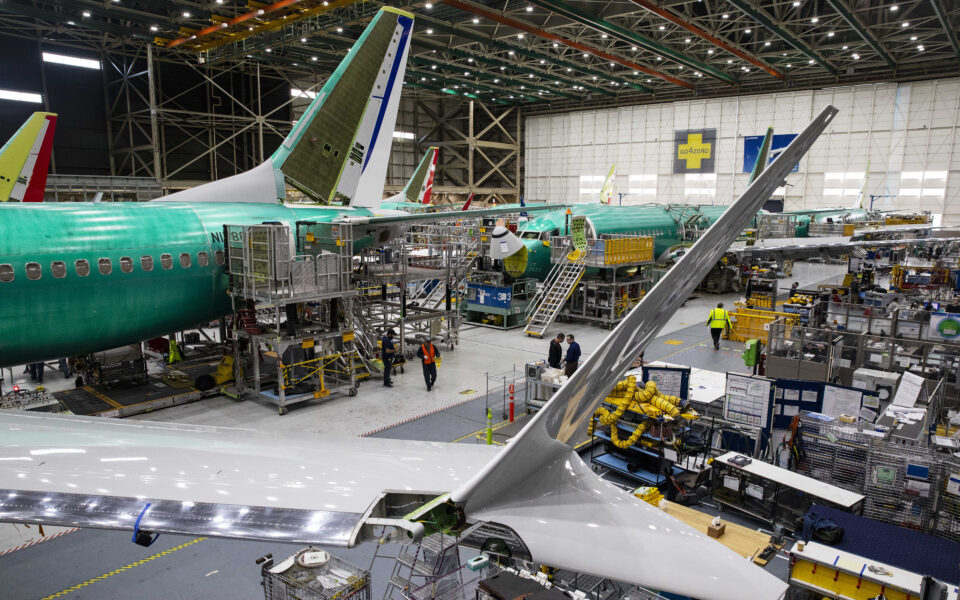

In February last year, a new Southwest Airlines Boeing 737 Max plane was on one of its first flights when an automated stabilizing system appeared to malfunction, forcing the pilots to make an emergency landing soon after they took off.
Less than two months later, an Alaska Airlines 737 Max plane with eight hours of total flight time was briefly grounded until mechanics resolved a problem with a fire detection system. And in November, an engine on a just-delivered United Airlines 737 Max failed at 37,000 feet.
These incidents, which the airlines disclosed to the Federal Aviation Administration, were not widely reported. There were no indications that anyone was in danger, and it was not clear who was ultimately responsible for those problems. But since Jan. 5, when a panel on a 2-month-old Alaska Airlines 737 Max 9 jet blew off in midair, episodes like these have taken on new resonance, raising further questions about the quality of the planes Boeing is producing.
“There’s a lot of areas where things don’t seem to be put together right in the first place,” said Joe Jacobsen, an engineer and aviation safety expert who spent more than a decade at Boeing and more than 25 years at the FAA.
“The theme is shortcuts everywhere – not doing the job right,” he added.
Such reports, and interviews with aviation safety experts and more than two dozen current and former Boeing employees, paint a worrying picture about a company long considered to be at the pinnacle of US engineering. They suggest that Boeing is struggling to improve quality years after two crashes of Max 8 planes in 2018 and 2019 killed nearly 350 people.
Some of the crucial layers of redundancies that are supposed to ensure that Boeing’s planes are safe appear to be strained, the people said. The experience level of Boeing’s workforce has dropped since the start of the pandemic. The inspection process intended to provide a vital check on work done by its mechanics has been weakened over the years. And some suppliers have struggled to adhere to quality standards while producing parts at the pace Boeing wanted them.
Under pressure to show regulators, airlines and passengers that the company is taking its latest crisis seriously, Boeing announced sweeping changes to its leadership Monday. CEO Dave Calhoun will leave at the end of the year, and Stan Deal, the head of the commercial planes division, which makes the 737 Max, retired immediately. The company’s chair, Larry Kellner, stepped down from that position and will not seek reelection to the board.
When he took the top job in January 2020, Calhoun said he was determined to improve the company’s safety culture. It added directors with engineering and safety expertise and created a safety committee on its board. Boeing said that it had increased the number of quality inspectors for commercial planes by 20% since 2019 and that inspections per plane had also risen.
After the Max 8 crashes, Boeing and its regulators focused most on the cause of those accidents: flawed design and software. Yet some current and former employees say problems with manufacturing quality were also apparent to them at the time and should have been to executives and regulators as well.
After the Jan. 5 mishap, a six-week FAA audit of Boeing’s 737 Max production documented dozens of lapses in Boeing’s quality-control practices. The agency has given the company three months, or until about late May, to address quality-control issues.
Federal officials have traced the panel blowout to Boeing’s factory in Renton, Washington, where the 737 Max is assembled. According to the National Transportation Safety Board, the panel was removed but appeared to have been reinstalled without bolts that secured it in place. That panel is known as a “door plug” and is used to cover the gap left by an unneeded emergency exit.
Current and former Boeing employees said the incident reflected long-standing problems. Several said employees often faced intense pressure to meet production deadlines, sometimes leading to questionable practices that they feared could compromise quality and safety.
Davin Fischer, a former mechanic in Renton, who also spoke to the Seattle TV station KIRO 7, said he noticed a cultural shift starting around 2017, when the company introduced the Max.
“They were trying to get the plane rate up and then just kept crunching, crunching and crunching to go faster, faster, faster,” he said.
The Max was introduced in response to a new fuel-efficient plane from European manufacturer Airbus. Boeing increased production from about 42 Max jets a month in early 2017 to about 52 the next year. That pace collapsed to virtually zero soon after the second crash, in Ethiopia, when regulators around the world grounded the plane. Flights aboard the Max resumed in late 2020, and the company began to increase production again to avoid falling further behind Airbus.
Now, some Boeing executives admit that they made mistakes.
“For years, we prioritized the movement of the airplane through the factory over getting it done right, and that’s got to change,” Brian West, the company’s chief financial officer, said at an investor conference last week.
Calhoun has also acknowledged that Boeing must improve but has defended the company’s approach to production. “Over the last several years, we’ve taken close care not to push the system too fast, and we have never hesitated to slow down, to halt production or to stop deliveries to take the time we need to get things right,” he said in January.
Current and former Boeing employees, most of whom spoke on the condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to speak to reporters and feared retaliation, offered examples of how quality has suffered over the years. Many said they still respected the company and its employees and wanted Boeing to succeed.
One quality manager in Washington who left Boeing last year said workers assembling planes would sometimes try to install parts that had not been logged or inspected, an attempt to save time by circumventing quality procedures intended to weed out defective or substandard components.
In one case, the employee said, a worker sent parts from a receiving area straight to the factory floor before a required inspection.
A worker currently at Boeing’s 787 Dreamliner factory in North Charleston, South Carolina, described seeing numerous problems on planes being assembled, including wires being routed incorrectly, raising the risk that they could rub against one another, resulting in damage.
Employees would also sometimes go “inspector shopping” to find someone who would approve work, the worker said.
Some of the concerns echoed accusations of quality lapses by several whistleblowers at Boeing’s South Carolina factory who spoke to the Times in 2019.
Several current and former employees in South Carolina and in Washington state said mechanics building planes were allowed in some instances to sign off on their own work. Such “self-verification” removes a crucial layer of quality control, they said.
Boeing said in a statement Wednesday that it had eliminated self-inspections in South Carolina in 2021 and that the practice accounted for less than 10% of inspections at other sites. The company inspects each plane before delivery to make sure that wire bundles are appropriately spaced, the statement said, and it does not allow inspector shopping.
Another factor at play in recent years has been that Boeing’s workers have less experience than they did before the pandemic.
When the pandemic took hold in early 2020, air travel plummeted, and many aviation executives believed it would take years for passengers to return in large numbers. Boeing began to cut jobs and encouraged workers to take buyouts or retire early. It ultimately lost about 19,000 employees companywide – including some with decades of experience.
In late 2022, Boeing lost veteran engineers who retired to lock in bigger monthly pension payments, which were tied to interest rates, according to the union that represents them, the Society of Professional Engineering Employees in Aerospace. More than 1,700 union members left the company that year, up from around 1,000 the year before. The members who left had been at the company for more than 23 years on average.
“We warned Boeing that it was going to lose a mountain of expertise, and we proposed some workarounds, but the company blew us off,” Ray Goforth, executive director of the union, said in a statement, adding that he thought the company used the retirements as an opportunity to cut costs by replacing veteran workers with “lower-paid entry-level engineers and technical workers.”
Boeing now employs 171,000 people, including in its commercial plane, defense, services and other divisions. That figure is up about 20% from the end of 2020. But many new workers are less seasoned, current and former employees said.
One Boeing employee who conducted quality inspections in Washington until last year said the company did not always provide new employees with sufficient training, sometimes leaving them to learn crucial skills from more experienced colleagues.
Boeing said that since Jan. 5, employees had asked for more training and that it was working on meeting those needs, including by adding training on the factory floor this month.
District 751 of the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers union, which represents more than 30,000 Boeing employees, said the average tenure of its members had dropped sharply in recent years. The proportion of its members who have less than six years of experience has roughly doubled to 50% from 25% before the pandemic.
After the Jan. 5 incident, Boeing announced changes to improve quality, including adding inspections at its factory in Renton and at the plant in Wichita, Kansas, owned by a supplier, Spirit AeroSystems, that makes the bodies of Max planes.
Boeing recently said it would no longer accept Max bodies from Spirit that still needed substantial work. It previously tolerated flaws that could be fixed later in the interest of keeping production on schedule.
Addressing its problems could take Boeing time, aviation experts said, frustrating airlines that need new planes.
Some carriers said recently that they were rejiggering their growth plans because they expected fewer planes from Boeing. Airlines may try to buy more from Airbus.
“They need to go slow to go fast,” Scott Kirby, the CEO of United Airlines, told investors this month, referring to Boeing. “I think they’re doing that.”
This article originally appeared in The New York Times.